| CPC H01F 41/026 (2013.01) [H01F 1/053 (2013.01); H01F 41/0293 (2013.01)] | 2 Claims |
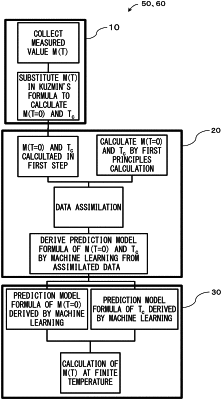
|
1. A rare earth sintered magnet comprising a single-phase magnetic phase that is prepared by sintering a magnetic powder comprising the single-phase magnetic phase, the single-phase magnetic phase in the magnetic powder having a size in the range of from 1 to 500 μm and having the composition represented by the formula (Nd(1−x−y)LaxCey)2(Fe(1−z)Coz)14B in an atomic ratio,
wherein x, y, and z in the formula in an atomic ratio satisfy a relationship represented by the following formulas (1) to (3), and a material parameters of the following formula (1) is 0.60,
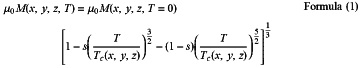 μ0: vacuum permeability (N/A2)
M(x,y,z,T): saturation magnetization at finite temperature (T)
M(x,y,z,T=0): saturation magnetization at absolute zero (T)
s: material parameter (−)
T: finite temperature (KS)
Tc: Curie temperature (K)
μ0M(x,y,z,T=0)=1.799−0.411x−0.451y−0.593z−0.011x2+0.002y2−0.070z2−0.002xy−0.058yz−0.040zx Formula (2)
μ0: vacuum permeability (N/A2)
M(x,y,z,T=0): saturation magnetization at absolute zero (T)
Tc(x,y,z)=588.894−5.825x−135.713y+506.799z+1.423x2+10.016y2−69.174z2+125.862xy+15.110yz−12.342zx Formula (3)
wherein z in the formula in an atomic ratio satisfies 0.30≤z≤0.40,
wherein x and y in the formula in an atomic ratio satisfy 0.03≤x≤0.50 and 0.03≤y ≤0.50, respectively, and
wherein the value represented by M(x, y, z, T=453)−M(x, y, z=0, T=453) is 0.02 to 0.24.
|