| CPC G06F 16/24553 (2019.01) [G06F 16/17 (2019.01); G06F 16/2246 (2019.01); G06F 16/24534 (2019.01)] | 20 Claims |
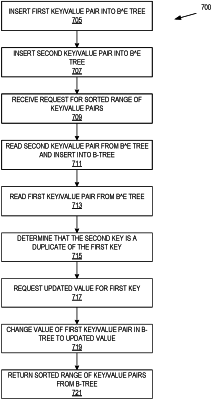
|
1. A computer-implemented method, comprising:
reading a first node in a tree data structure from a first memory, the first node including a first approximate membership query data structure (“AMQ”), a first plurality of child pointers, a first plurality of pivot values, and a first buffer storing pending insertion messages for a subtree rooted at the first node, wherein the first AMQ includes approximate membership of the first buffer;
maintaining an invariant that the AMQ will not return false negatives when queried for a key value, including determining that a quantity of child pointers in the first plurality of child pointers exceeds a maximum number of child pointers, and in response to the determining:
splitting, using a pivot value in the first plurality of pivot values the first node into a second node and a third node, wherein a first portion of the first plurality of child pointers are included in the second node and a second portion of the first plurality of child pointers are included in the third node;
splitting, using the pivot value, the first buffer into a second buffer and a third buffer, wherein the second node includes the second buffer and the third node includes the third buffer; and
splitting the first AMQ between the second node as a second AMQ and the third node as a third AMQ, wherein the second AMQ is associated with key values added to the second node having a first pivot range from a first child key value to the pivot value and the third AMQ is associated with key values added to the third node having a second pivot range from after the pivot value to a last child key value, and wherein the each of the second AMQ and the third AMQ approximates a portion of the first buffer membership corresponding, respectively, to the first pivot range and the second pivot range.
|