| CPC G05D 1/0202 (2013.01) [B64C 39/02 (2013.01); B64D 47/08 (2013.01); B64U 2101/30 (2023.01)] | 15 Claims |
|
1. An unmanned aerial vehicle, comprising:
a wireless communication circuit;
at least one sensor;
a processor operatively connected to the wireless communication circuit and the at least one sensor; and
a memory operatively connected to the processor,
wherein the memory stores instructions executable by the processor to cause the unmanned aerial vehicle to:
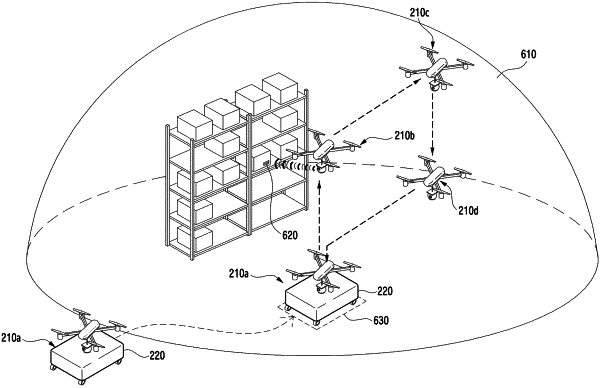
receive a first moving command transmitted from an automated guided vehicle, when the automated guided vehicle on which the unmanned aerial vehicle is placed is moved to a designated position, wherein the first moving command include a take-off command and a command for moving to a first target area;
in response to the first moving command, take off from the automated guided vehicle and move to the first target area;
obtain position-unrelated sensing information via the at least one sensor, while moving according to the first moving command; and
transmit the position-unrelated sensing information to the automated guided vehicle, such that the automated guided vehicle determines a position of the unmanned aerial vehicle using the position-unrelated sensing information, and
receive, from the automated guided vehicle, a second moving command for moving to a second target area, when it is determined by the automated guided vehicle that the unmanned aerial vehicle is positioned to the first target area.
|