| CPC G05B 19/4155 (2013.01) [B25J 9/0006 (2013.01); B25J 9/1656 (2013.01); B25J 13/00 (2013.01); G06F 3/015 (2013.01); G05B 2219/39292 (2013.01)] | 19 Claims |
|
1. A method, comprising:
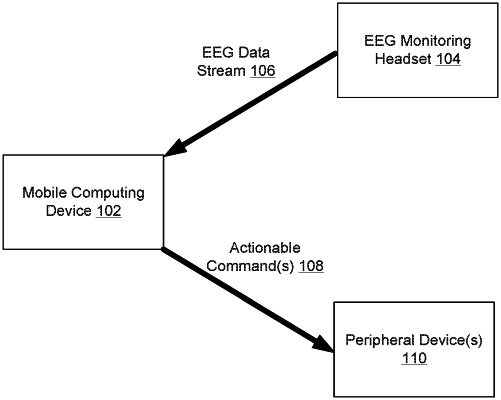
receiving, by a mobile computing device from an electroencephalogram (EEG) monitoring headset, an incoming wireless communication signal comprising an EEG data stream;
processing, by an application running on the mobile computing device, the received EEG data stream to determine at least one actionable command;
transmitting, by the mobile computing device to a robotic device, a first wireless communication control signal to cause active operation of the robotic device based on the at least one actionable command; and
transmitting, by the mobile computing device to a sensory motor feedback device, a second wireless communication control signal to cause the sensory motor feedback device to provide tactical feedback during the active operation of the robotic device.
|