| CPC G03H 1/0443 (2013.01) [G03H 1/06 (2013.01); G03H 2001/2265 (2013.01); G03H 2222/31 (2013.01); G03H 2223/20 (2013.01)] | 4 Claims |
|
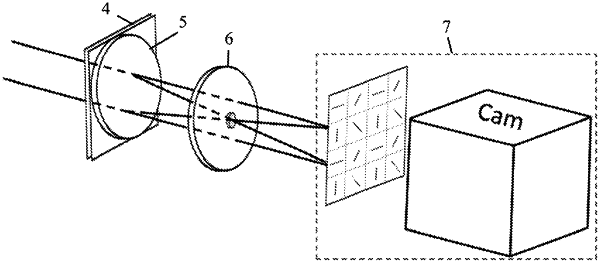
1. A holographic device, comprising
a polarization-oriented planar lens,
a focusing element, the focusing element being attached to the polarization-oriented planar lens with a separation distance of 0 mm and comprising a focal point,
a half-wave plate with a small hole, wherein the focal point of the focusing element is in the small hole of the half-wave plate, and
a polarization imaging camera,
wherein an incident light passes through the polarization-oriented planar lens and the focusing element, and is divided into a left-handed circularly polarized light and a right-handed circularly polarized light with different polarization, and one of the left-handed circularly polarized light and the right-handed circularly polarized light is a focused beam, and the other of the left-handed circularly polarized light and right-handed circularly polarized light is a parallel or divergent beam,
the focused beam passes through the small hole of the half-wave plate,
the parallel or divergent beam passes through the half-wave plate, wherein polarization of the parallel or divergent beam is changed to be consistent with the polarization of the focused beam so that both become left-handed or right-handed circularly polarized beams and are overlapped in the polarization imaging camera to obtain an interferometric pattern of recorded object information.
|