| CPC G01S 13/90 (2013.01) [G01S 13/867 (2013.01); G01S 13/955 (2013.01); G01S 7/292 (2013.01)] | 7 Claims |
|
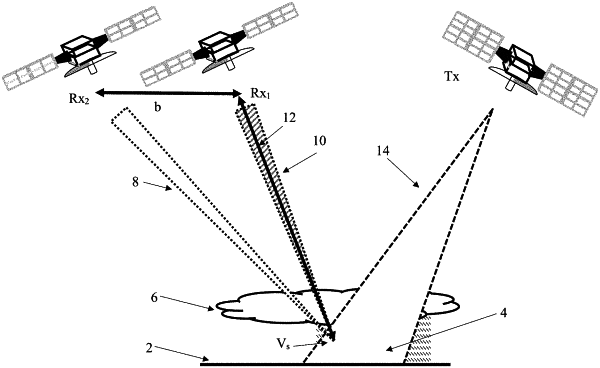
1. A synthetic aperture RADAR method comprising,
providing at least one transmitting low earth orbit satellite;
providing at least two receiving low earth orbit satellites;
remotely coupling the at least one transmitting low earth orbit satellite with the at least two receiving low earth orbit satellites;
flying the at least one transmitting low earth orbit satellite and the at least two receiving low earth orbit satellites in formation;
synchronizing a timing of the at least one transmitting low earth orbit satellite and the at least two receiving low earth orbit satellites;
collecting and resolving a plurality of two-dimensional intensity images via the at least two receiving low earth orbit satellites in an along-track dimension;
operating the at least two receiving low earth orbit satellites in a spotlight synthetic aperture RADAR mode;
aggregating the plurality of two-dimensional intensity images to increase a signal to noise;
collecting a plurality of cross-correlation interferograms in a cross-track dimension, formed by echoes from a precipitation field observed at each receiver when using range-resolving waveforms emitted from the at least one transmitting low earth orbit satellite; and
creating a three-dimensional precipitation field using the aggregated two-dimensional intensity images derived from the plurality of cross-correlation interferograms obtained when collecting radar echoes from a scene observed through diverse angles with spatial intensity variations in a third, or the along-track, dimension recoverable through tomographic processing.
|