| CPC G01N 35/1002 (2013.01) [G01N 35/00603 (2013.01); G01N 35/1016 (2013.01); G01N 2035/1018 (2013.01)] | 6 Claims |
|
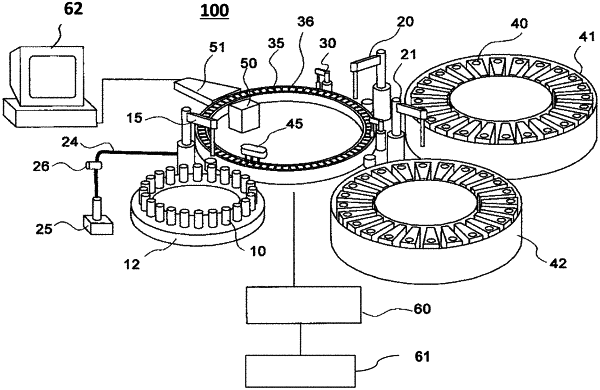
1. An automatic analyzer comprising:
a liquid dispensing mechanism that sucks a sample or a reagent that is a liquid contained in a container;
a pressure sensor that measures a change of a pressure in a probe provided at the liquid dispensing mechanism;
an analysis section that analyzes the sample;
a controller that controls the liquid dispensing mechanism to perform suction operations comprising individual suctions, and the analysis section to perform a sample analysis operation,
wherein the controller is configured to, for each suction operation planned:
(a) store an initial cumulative number of determined air suction abnormalities per liquid and a predetermined allowable cumulative number of air suction abnormalities, the predetermined allowable cumulative number being equal to or greater than 2;
(b) determine whether suction by the probe is liquid suction that is normal suction or air suction that is abnormal suction on the basis of the change of the pressure measured by the pressure sensor;
(c) update the stored cumulative number of the air suction abnormalities in the event an abnormal suction has been determined in step b) and store the updated cumulative number even if the air suction abnormalities are not consecutive in a course of the suction operation of the liquid by the probe with respect to a number of measurement items for the same liquid;
(d) repeat steps (b)-(c) for each individual suction in the suction operation without washing the liquid dispensing mechanism until the updated cumulative number reaches the predetermined allowable cumulative number; and
(e) cancel requests of the measurement items planned for the liquid and cause another suction operation to be performed on another liquid planned next upon determining the updated cumulative number reaches the predetermined allowable cumulative number.
|