| CPC G01N 33/2847 (2013.01) [E21B 47/06 (2013.01); E21B 47/07 (2020.05); G01N 33/2823 (2013.01); E21B 2200/20 (2020.05); E21B 2200/22 (2020.05)] | 18 Claims |
|
1. An intelligent water cut estimation system comprising at least two pressure sensors, a neural network model, and a data processor, wherein:
the at least two pressure sensors are configured to generate pressure data respectively associated with two points of a well bore;
the neural network model comprises one or more parameters indicative of water cut associated with a well bore; and
the data processor is communicatively coupled to the at least two pressure sensors and the neural network model and is operable to:
receive pressure data from the at least two pressure sensors respectively indicative of the pressure at each of the two points of the well bore,
determine a pressure drop between the two points based on the received pressure data from the at least two pressure sensors,
generate an input water cut estimate,
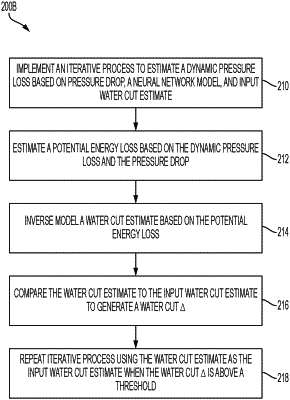
estimate a dynamic pressure loss based on the pressure drop, the one or more parameters of the neural network model, and the input water cut estimate to initiate an iterative process,
estimate a potential energy loss based on the dynamic pressure loss and the pressure drop,
inverse model a water cut estimate based on the potential energy loss,
compare the water cut estimate to the input water cut estimate to generate a water cut Δ,
utilize the water cut estimate as the input water cut estimate for the iterative process when the water cut Δ exceeds a threshold, and
continue the iterative process until the water cut Δ is below the threshold.
|