| CPC G01N 25/18 (2013.01) [E21B 33/14 (2013.01); E21B 49/02 (2013.01); G01N 33/383 (2013.01)] | 8 Claims |
|
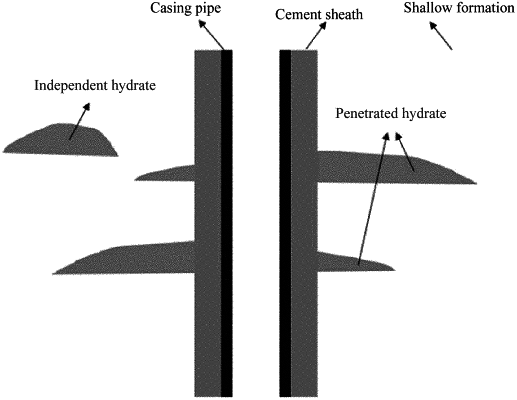
1. A design method of a cement for well cementing in a penetrated hydrate layer, wherein a low-hydration, early-strength, and heat-insulating cement slurry system is used during the well cementing in the penetrated hydrate later, and the penetrated hydrate layer is a hydrate layer penetrated by a casing pipe, comprising the following steps:
(1) collecting a formation sample of a cementing-target penetrated hydrate layer, testing physical parameters of the formation sample, and acquiring environmental parameters of the cementing-target penetrated hydrate layer;
(2) analyzing the physical parameters of the formation sample, and determining early strength performance requirements, hydration heat performance requirements, and heat insulation performance requirements of a cement slurry meeting cementing conditions based on field operation requirements;
(3) according to the early strength performance requirements of the cement slurry, testing effects of various early-strength agents, and selecting an early-strength agent with optimal performance from the various early-strength agents;
(4) according to the hydration heat performance requirements of the cement slurry, testing effects of various low-hydration-heat materials, and selecting a low-hydration-heat material with optimal performance from the various low-hydration-heat materials;
(5) according to the heat insulation performance requirements of the cement slurry, testing effects of various heat-insulating materials, and selecting a heat-insulating material with optimal performance from the various heat-insulating materials;
(6) preparing the early-strength agent with the optimal performance, the low-hydration-heat material with the optimal performance, the heat-insulating material with the optimal performance and the cement slurry into the low-hydration, early-strength, and heat-insulating cement slurry system to adjust performance of the cement slurry, such that the cement slurry has low hydration, early strength, and heat insulation performance and meets requirements of a cementing construction;
(7) using a performance evaluation device of a cement for well cementing in a penetrated hydrate layer to simulate a cementing process of the penetrated hydrate layer, and determining whether performance of the low-hydration, early-strength, and heat-insulating cement slurry system meets the requirements of the cementing construction; and if the requirements of the cementing construction are met, proceeding to step (8), and if the requirements of the cementing construction are not met, repeating steps (3) to (6); and
(8) estimating a cement slurry injection volume required by the cementing-target penetrated hydrate layer, and injecting the low-hydration, early-strength, and heat-insulating cement slurry system meeting the requirements of the cementing construction into the formation sample in a form of a displacement liquid according to field operation conditions and corresponding construction parameters until the cement slurry reaches a predetermined solidification range.
|