| CPC G01N 21/6456 (2013.01) [G01N 33/543 (2013.01)] | 23 Claims |
|
1. A method for analyzing the results of a ligand-receptor binding assay comprising the steps of:
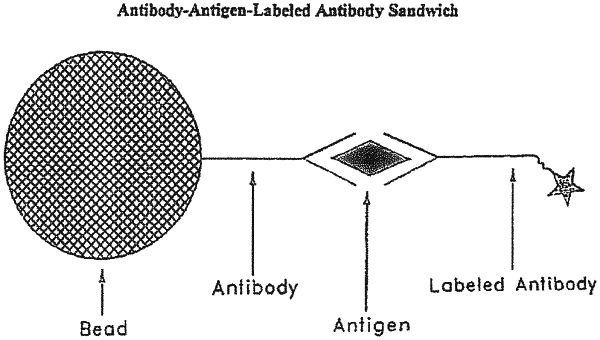
(a) providing the results of a ligand-receptor binding assay wherein the ligand-receptor binding assay comprises combining in a reaction mixture (i) a sample suspected of containing a ligand, (ii) a first receptor attached to a microparticle that binds to the ligand, and (iii) a fluorescently labeled second receptor that binds to the ligand, and allowing formation of a complex comprising the microparticle attached to the first receptor, the ligand, and the fluorescently labeled second receptor by acquiring a white light image of the reaction mixture in order to determine the location of microparticles and a fluorescence image to determine the location of the fluorescently labeled second receptor;
(b) selecting at least one region of interest from the images wherein the at least one region of interest is a region from which light signals emanate from the complex; and
(c) qualifying the results of a ligand-receptor binding assay by:
(i) selecting pixels in the at least one region of interest for analysis;
(ii) calculating and recording the average and variance of the counts per pixel for the pixels selected in step (i);
(iii) omitting pixels that have counts greater than or less than a specified variance; and
(iv) calculating average counts per pixel of the remaining pixels.
|