| CPC G01N 21/1702 (2013.01) [G01N 21/39 (2013.01); G01N 2021/1704 (2013.01); G01N 2021/396 (2013.01)] | 13 Claims |
|
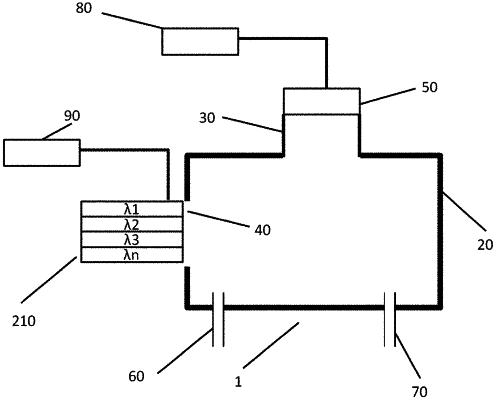
1. A photo-acoustic gas sensor comprising:
a cell forming an acoustic resonator, comprising a gas inlet duct, a gas outlet duct and at least one aperture called the laser inlet;
at least one electrically pumped laser source;
at least one electro-acoustic transducer; and
a supply circuit that generates a pulsed electric current, called the generation electric current, that pumps the one or more laser sources and that is configured to cause the one or more laser sources to operate in pulsed mode, the repetition frequency of the laser pulses being at least 10 times, preferably 100 times, more preferably 1000 times higher than the resonant frequency of the cell;
wherein the supply circuit is configured to furthermore generate a current, called the base current, that takes non-zero values between laser pulses with a magnitude lower than the magnitude of the generation current during the laser pulses, the magnitude of the base current being modulated so that the one or more laser sources emit, into the cell, light radiation having a wavelength that varies periodically about a central wavelength so as to take, at regular intervals, a value specifically suitable for excitation of a gas to be detected, whereby an interaction between the light radiation and the gas to be detected contained in the cell induces the generation of acoustic waves at a resonant frequency of the cell, the electro-acoustic transducer being arranged so as to make contact with the acoustic waves generated in the cell.
|