| CPC G01L 1/18 (2013.01) [G01L 1/142 (2013.01); A61B 5/1125 (2013.01); A61B 5/682 (2013.01); A61B 5/6821 (2013.01); A61B 5/6823 (2013.01); A61B 5/6826 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
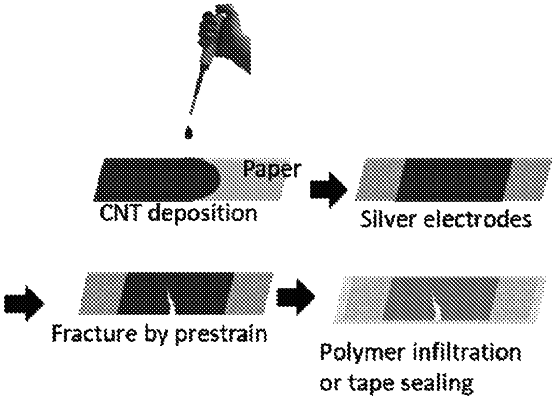
19. A method of making a sensor comprising applying a unidirectional tensile force to a precursor composite substrate thereby inducing a fracture to form a fractured composite substrate, wherein the precursor composite substrate comprises:
a template material comprising a plurality of insulating fibers;
a plurality of carbon nanotubes bonded to the insulating fibers forming a nanotube coating on the insulating fibers;
a first electrode coupled to the nanotube coating on one side of the fracture; and
a second electrode coupled to the nanotube coating on an opposite side of the fracture; and
wherein the plurality of insulating fibers form a plurality of crossbar junctions at a site of the fracture.
|