| CPC F24F 11/38 (2018.01) [F24F 2140/12 (2018.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
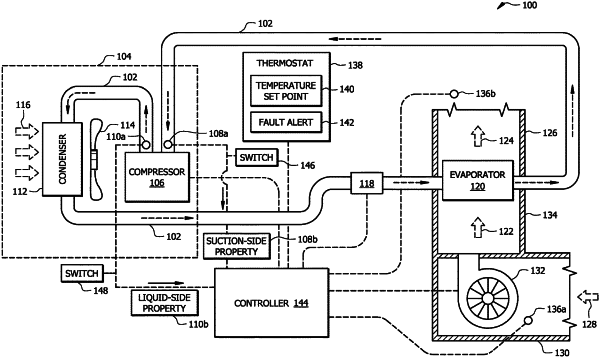
1. A heating, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC) system comprising:
a refrigerant conduit subsystem configured to allow a flow of refrigerant through the HVAC system;
a compressor configured to receive refrigerant and direct the refrigerant to flow through a refrigerant conduit subsystem;
an evaporator configured to receive the refrigerant and allow heat transfer between the refrigerant and a flow air across the evaporator;
a blower configured to provide the flow of air across the evaporator;
a suction-side sensor positioned and configured to measure a suction-side property associated with refrigerant provided to an inlet of the compressor, wherein the suction-side property comprises at least one of a suction-side temperature or a suction-side pressure;
a shutoff switch communicatively coupled to the suction-side sensor and configured to be tripped and automatically stop operation of the compressor and blower in response to determining that the suction-side property is less than a predefined minimum value;
a liquid-side sensor positioned and configured to measure a liquid-side property associated with the refrigerant provided from an outlet of the compressor, wherein the liquid-side property comprises at least one of a liquid-side temperature or a liquid-side pressure; and
a controller communicatively coupled to the shutoff switch and the liquid-side sensor, the controller configured to:
store measurements of the liquid-side property over an initial period of time;
detect that the shutoff switch is tripped at a first time stamp corresponding to an end of the initial period of time;
access the measurements of the liquid-side property;
determine, based on the measurements of the liquid-side property, that the liquid-side property has an increasing trend; and
in response to determining that the liquid-side property has the increasing trend, determine that a blockage of the refrigerant conduit subsystem caused the shutoff switch to trip.
|