| CPC C12N 15/1093 (2013.01) [C12N 15/1031 (2013.01); C12Q 1/68 (2013.01); C12Q 2521/101 (2013.01); C12Q 2533/101 (2013.01); C12Q 2535/125 (2013.01)] | 33 Claims |
|
1. A method for connecting separated regions of DNA molecules in a biological sample of a subject, the method comprising:
partitioning a plurality of DNA molecules from the biological sample into a plurality of compartments, wherein a first compartment of the plurality of compartments includes:
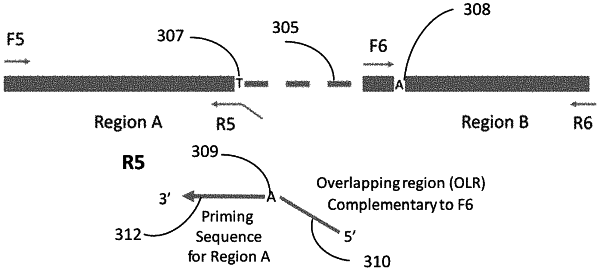
a first DNA molecule having a region A and a region B separated by an intermediate region,
a polymerase having a bias for adding a particular nucleotide at an overhang position,
a reverse primer R1 having a first portion complementary to an ending sequence of the region A, the reverse primer R1 including a second portion having an overlapping sequence, and
a forward primer F2 having a first portion complementary to a starting sequence of the region B, the forward primer F2 including a complementary overlapping sequence that is complementary to the overlapping sequence;
amplifying, using the polymerase and the reverse primer R1, the region A to obtain a first set of amplicons having the particular nucleotide at a first 3′ end and having a complementary nucleotide between sequence strings corresponding to the first portion and the second portion of the reverse primer R1, the complementary nucleotide being complementary to the particular nucleotide;
amplifying, using the polymerase and the forward primer F2, the region B to obtain a second set of amplicons having the particular nucleotide at a second 3′ end and having the complementary nucleotide on an opposite end of the overlapping sequence; and
extending, using the polymerase, the first set of amplicons to include the region B and the second set of amplicons to include the region A, thereby obtaining extended amplicons that include the region A and the region B and exclude the intermediate region.
|