| CPC A61B 17/1355 (2013.01) [A61B 5/026 (2013.01); A61B 5/6824 (2013.01); A61B 5/6828 (2013.01); A61B 2017/00022 (2013.01)] | 19 Claims |
|
1. An apparatus for maintaining cerebral circulation in a patient above a baseline flow rate during treatment, the apparatus comprising:
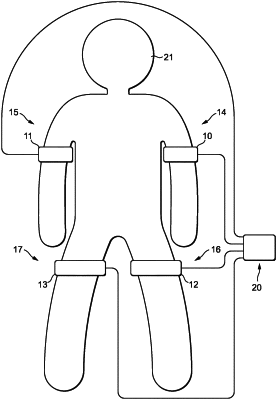
(a) a plurality of compression cuffs, each cuff being inflatable and deflatable and each cuff being positionable, in use, around a respective limb of a patient and inflatable to exert a pressure upon the limb sufficient to reduce limb blood flow below a point at which the cuff is positioned;
(b) a control module to which the cuffs are attachable, the control module comprising fil a pump with which each cuff is in fluid communication, (ii) an imaging device adapted to determine where an occlusion is present in the cerebral circulation, and (iii) a valve arrangement associated with each cuff to control flow of fluid to and from each cuff, the control module being adapted to inflate and deflate each cuff independently of the others; and
(c) a cerebral blood flow monitoring apparatus adapted to detect the baseline flow rate in the cerebral circulation and to repeatedly measure or continuously monitor flow rate in the cerebral circulation during treatment of the patient,
wherein the control module is in operative communication with the cerebral blood flow monitoring apparatus, such that the control module is adapted to inflate one or more cuffs to reduce the respective limb blood flow below the point around the respective limb at which the inflated cuff or each inflated cuff is positioned and maintain inflation of the or each cuff for a predetermined period, to thereby elevate the cerebral circulation from the baseline flow rate to an increased flow rate, and thereafter control inflation of the plurality of cuffs to maintain the measured or monitored flow rate above the baseline flow rate during treatment, by reducing limb blood flow and augmenting cerebral circulation.
|