| CPC A61B 5/7275 (2013.01) [A61B 5/7267 (2013.01); A61B 6/032 (2013.01); A61B 6/50 (2013.01); G06F 18/214 (2023.01); G06T 7/0012 (2013.01); G06T 7/11 (2017.01); G06T 7/62 (2017.01); G16H 30/40 (2018.01); G16H 50/20 (2018.01); G06T 2207/10081 (2013.01); G06T 2207/10116 (2013.01); G06T 2207/20081 (2013.01); G06T 2207/20084 (2013.01); G06T 2207/20221 (2013.01); G06T 2207/30061 (2013.01); G06V 2201/031 (2022.01)] | 24 Claims |
|
1. A computer implemented method, comprising:
receiving an input medical image in a first modality;
segmenting lungs from the input medical image using a trained lung segmentation network;
segmenting abnormality patterns associated with a disease from the input medical image using a trained abnormality pattern segmentation network; and
determining an assessment of the disease based on the segmented lungs and the segmented abnormality patterns,
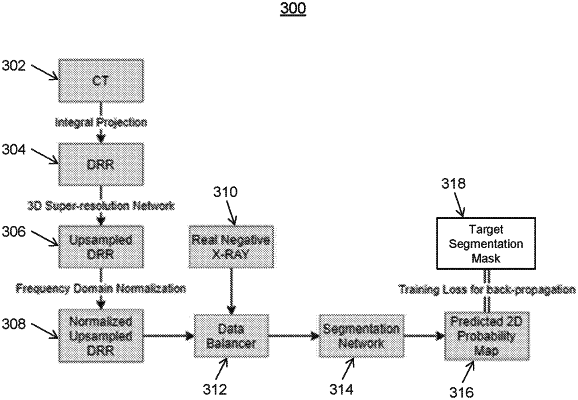
wherein the trained lung segmentation network and the trained abnormality pattern segmentation network are trained based on 1) synthesized images in the first modality generated from training images of an anatomical object in a second modality and 2) target segmentation masks for the synthesized images, the target segmentation masks generated by:
projecting regions of the training images within their corresponding training segmentation masks to a two dimensional mask, and
assigning each pixel in the two dimensional mask a value corresponding to a sum of intensity values of voxels in the training images that are within the anatomical object and penetrated by the projection for that pixel.
|