| CPC A61B 5/168 (2013.01) [A61B 5/30 (2021.01); A61B 5/369 (2021.01); A61B 5/7246 (2013.01); A61B 5/7264 (2013.01); A61B 5/742 (2013.01); G16H 50/20 (2018.01)] | 16 Claims |
|
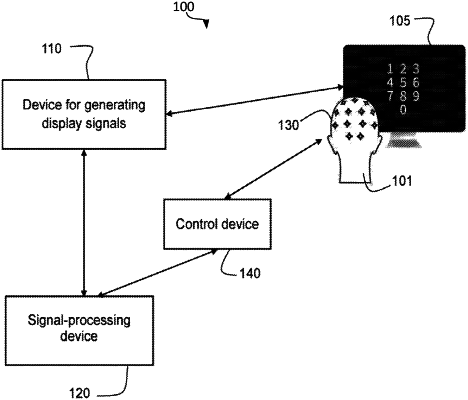
1. A method for determining a focus of visual attention of an individual from electroencephalographic signals, the method comprising;
generating a set of at least one visual stimulus to be displayed based on at least one graphical object of a human-machine interface of a computational device, at least one elementary transformation, and a set of at least one modulation signal, a visual stimulus of the set of at least one visual stimulus being an animated graphical object obtained by applying to a graphical object a temporal succession of elementary transformations that is temporally parameterized by a corresponding modulation signal;
presenting the at least one visual stimulus in a display to the individual;
recording a plurality of electroencephalographic signals produced by the individual while the individual is paying attention to the displayed at least one visual stimulus; and
performing, in real-time, operations comprising:
reconstructing a modulation signal from the plurality of electroencephalographic signals produced by the individual in order to obtain a reconstructed modulation signal;
computing a degree of statistical dependence between the reconstructed modulation signal and each modulation signal of the set of at least one modulation signal;
in response to identifying at least one visual stimulus corresponding to a modulation signal for which the degree of statistical dependence is higher than a first threshold, triggering one or more operations of the computational device.
|