| CPC A61B 1/00082 (2013.01) [A61B 5/027 (2013.01); A61B 5/1459 (2013.01); A61B 18/20 (2013.01); A61B 2017/00057 (2013.01)] | 30 Claims |
|
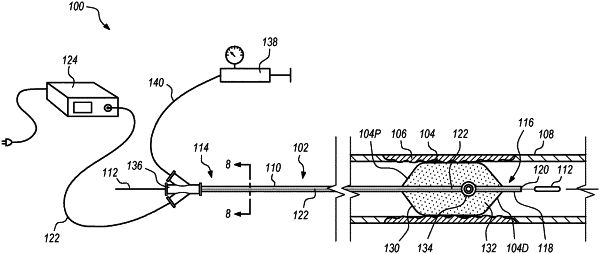
1. A catheter system for treating a treatment site within or adjacent to a blood vessel, the catheter system comprising:
a power source;
a light guide that receives power from the power source, the light guide having a distal tip, the light guide emitting light energy in a direction away from the distal tip; and
a plasma target that is spaced apart from the distal tip of the light guide by a target gap distance, the plasma target being configured to receive light energy from the light guide so that a plasma is generated at the plasma target upon receiving the light energy from the light guide, the plasma target being at least partially formed from one of tungsten, tantalum, platinum, molybdenum, niobium, and iridium.
|