| CPC H01S 3/10061 (2013.01) [G02F 1/0136 (2013.01); H01S 3/06716 (2013.01); H01S 3/06791 (2013.01); H01S 3/08013 (2013.01); H01S 3/1109 (2013.01); H01S 3/1115 (2013.01); H01S 3/1608 (2013.01)] | 11 Claims |
|
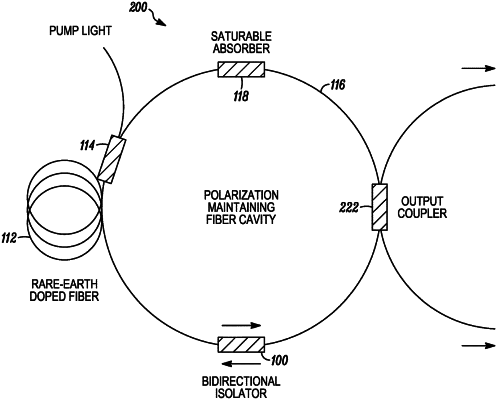
1. A bidirectional mode-locked laser, comprising:
an optical fiber cavity that includes polarization-maintaining optical fiber;
a gain element located in the optical fiber cavity for amplifying optical signals propagating in the optical fiber cavity;
a mode-locking element located in the optical fiber cavity for mode-locking the laser cavity to thereby generate first and second optical pulse trains traveling in opposite directions in the optical fiber cavity; and
a bidirectional polarization element located in the optical fiber cavity, the bidirectional polarization element being configured to only allow optical energy that is in a first polarization state to propagate therethrough in first and second directions, the first and second directions being opposite to one another and the first polarization state being orthogonal to a second polarization state, the bidirectional polarization element being located between two polarization-maintaining optical fiber segments in the optical fiber cavity that are oriented with respect to one another so that optical energy propagating in the respective optical fiber segments are in orthogonal polarization states with respect to one another, wherein the bidirectional polarization element outputs the optical energy in the second polarization state orthogonal to the first polarization state.
|