| CPC H01M 50/411 (2021.01) [C08L 27/16 (2013.01); H01M 10/0565 (2013.01); H01M 50/403 (2021.01); H01M 2300/0082 (2013.01)] | 31 Claims |
|
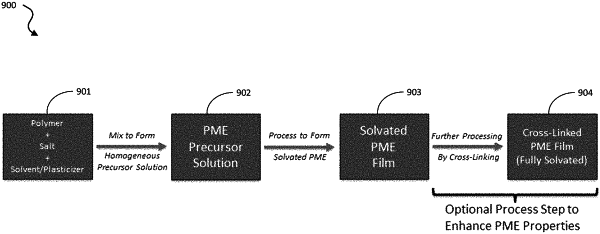
1. A method of preparing a polymer matrix electrolyte (PME) precursor solution, the method comprising:
(a) preparing a first solution comprising at least one polymer and a solvent;
(b) preparing a second solution comprising a lithium salt, and a solvent; and
(c) mixing the first solution with the second solution to form the PME precursor solution, wherein the PME precursor solution is used for making a PME membrane having a mechanical strength of about 105 to about 1010 pascals (Pa), wherein the PME membrane has a storage modulus of about 3.33×108 Pa and a loss modulus of 2.82×107 Pa at 20° C., and wherein the PME membrane has no or substantially no pores.
|