| CPC G06F 9/5094 (2013.01) [G06F 9/5077 (2013.01)] | 18 Claims |
|
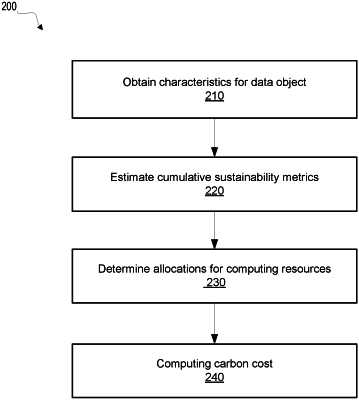
1. A computer-implemented method for allocating computing resources, comprising:
obtaining a plurality of characteristics of a data object;
estimating, from the obtained characteristics, one or more cumulative sustainability metrics characterizing one or more categories of energy consumption during a life-cycle of the data object, wherein the one or more cumulative sustainability metrics comprise one or more of:
a cumulative functional sustainability metric characterizing energy consumption related to information contents of the data object during the life-cycle of the data object;
a cumulative structural sustainability metric characterizing energy consumption related to data types of the data object during the life-cycle of the data object;
a cumulative operational sustainability metric characterizing energy consumption related to operations for accessing the data object during the life-cycle of the data object; or
a cumulative strategic sustainability metric characterizing energy consumption related to maintaining strategic criticality of the data object during the life-cycle of the data object; and
wherein the estimating comprises:
estimating, from one or more of the plurality of characteristics of the data object, one or more of:
a type heterogeneity parameter characterizing a variation of types of constituent elements in the data object;
a compressibility parameter characterizing an intrinsic redundancy of the constituent elements in the data object; or
a type-complexity parameter characterizing a structural complexity of the constituent elements in the data object; and
estimating the cumulative structural sustainability metric from one or more of the type heterogeneity parameter, the compressibility parameter, or the type-complexity parameter; and
determining, from the cumulative sustainability metrics, allocations of one or more computing resources to the data object to optimize one or more objectives including minimizing a cumulative carbon cost during the life-cycle of the data object.
|