| CPC G01R 33/58 (2013.01) [G01R 33/5608 (2013.01); G06N 3/048 (2023.01); G06N 3/08 (2013.01); G01R 33/56545 (2013.01)] | 21 Claims |
|
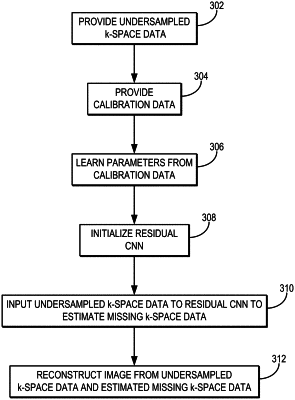
1. A method for reconstructing an image from undersampled k-space data acquired with a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system, the steps of the method comprising:
(a) providing to a computer system, undersampled k-space data and calibration data acquired with an MRI system;
(b) processing the calibration data with a computer system to learn parameters for a residual machine learning algorithm implemented with a hardware processor and memory of the computer system, wherein the residual machine learning algorithm comprises a linear residual connection and a multi-layer portion having at least one nonlinear processing layer;
(c) estimating missing k-space data by inputting the undersampled k-space data to the residual machine learning algorithm, generating output as the missing k-space data; and
(d) reconstructing an image from the undersampled k-space data and the estimated missing k-space data.
|