| CPC F24F 11/32 (2018.01) [G05B 15/02 (2013.01); G08B 21/14 (2013.01); G08B 21/182 (2013.01); H04W 4/12 (2013.01)] | 18 Claims |
|
1. A method comprising:
maintaining, in a memory, a set of associations between two or more carbon monoxide (CO) sensors and two or more CO sources;
receiving, by processing circuitry, data from a first CO sensor of the two or more CO sensors;
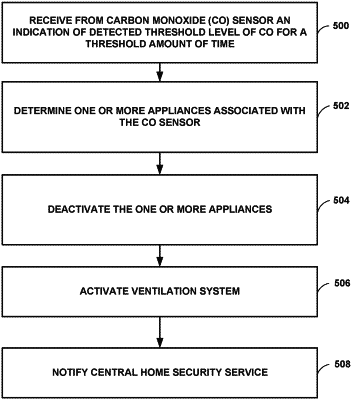
determining, by the processing circuitry and based on the data received from the first CO sensor, that a first level of CO detected by the first CO sensor has exceeded a first threshold level of CO for a first threshold period of time;
identifying, based on the set of associations, a first subset of CO sources associated with the first CO sensor, wherein the first subset of CO sources comprises at least one CO source of the two or more CO sources and fewer than all of the two or more CO sources;
in response to determining that the first level of CO detected by the first CO sensor currently exceeds the first threshold level of CO and has exceeded the first threshold level of CO for the first threshold period of time, disabling the first subset of CO sources, wherein disabling the first subset of CO sources comprises transmitting a first signal that causes the first subset of CO sources to be disabled;
in response to disabling the first subset of CO sources, detecting, by the first CO sensor, a second level of CO less than the first level of CO;
determining, based on the second level, that at least one appliance of the first subset of CO sources was a cause of the first level of CO;
transmitting a second signal that causes each of the first subset of CO sources to be reactivated one-at-a-time in order to determine which appliance of the first subset of CO sources was the cause of the first level of CO; and
transmitting a third signal that causes each of the first subset of CO sources except for the determined cause of the first level of CO to be reactivated.
|