| CPC C08C 19/02 (2013.01) [B01J 31/0204 (2013.01); B01J 31/2217 (2013.01); B01J 31/2273 (2013.01); B01J 31/2295 (2013.01); C08L 15/005 (2013.01); B01J 2231/643 (2013.01); B01J 2531/007 (2013.01); B01J 2531/821 (2013.01)] | 18 Claims |
|
1. A process for hydrogenating a nitrile rubber comprising:
a) preparing a hydrogenation catalyst composition by contacting a complex hydrogenation catalyst of the general formula (IA) or (IB)
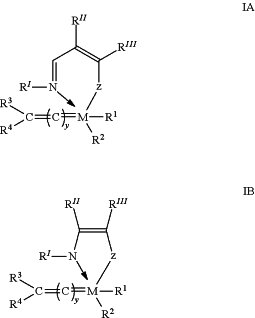 M is ruthenium;
z is selected from the group consisting of oxygen, sulphur, selenium, NR″″, PR″″, AsR″″ and SbR″″; R″, R′″ and R″″ are each a radical independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, C1-6 alkyl, C3-8 cycloalkyl, C1-6 alkyl-C1-6 alkoxysilyl, C1-6 alkyl-aryloxysilyl, C1-6 alkyl-C3-10 cycloalkoxysilyl, aryl and heteroaryl, or R″ and R′″ together form an aryl or heteroaryl radical, each said radical (when different from hydrogen) being optionally substituted with one or more, preferably 1 to 3, substituents R5 each independently selected from the group consisting of halogen atoms, C1-6 alkyl, C1-6 alkoxy, aryl, alkylsulfonate, arylsulfonate, alkylphosphonate, arylphosphonate, C1-6 alkyl-C1-6 alkoxysilyl, C1-6 alkyl-aryloxysilyl, C1-6 alkyl-C3-10 cycloalkoxysilyl, alkylammonium and arylammonium;
R′ is either methyl, phenyl or substituted phenyl (e.g. dimethyl bromo phenyl or diisopropylphenyl) when included in a compound having the general formula (IA) or, is methylene or benzylidene when included in a compound having the general formula (IB);
R1 is an electron donating complex ligand, which could be linked or not linked with R2 to form a cyclic structure;
R2 is an anionic ligand;
R3 and R4 are each hydrogen or a radical selected from the group consisting of C1-20 alkyl, C2-20 alkenyl, C2-20 alkynyl, C1-20 carboxylate, C1-20 alkoxy, C2-20 alkenyloxy, C2-20 alkynyloxy, aryl, aryloxy, C1-20 alkoxycarbonyl, C1-8 alkylthio, C1-20 alkylsulfonyl, C1-20 alkylsulfinyl C1-20 alkylsulfonate, arylsulfonate, C1-20 alkylphosphonate, arylphosphonate, C1-20 alkylammonium and arylammonium;
R′ and one of R3 and R4 may be bonded to each other to form a bidentate ligand;
R′″ and R″″ may be bonded to each other to form an aliphatic ring system including a heteroatom selected from the group consisting of nitrogen, phosphorous, arsenic and antimony;
R3 and R4 together may form a fused aromatic ring system having the formula (VI)
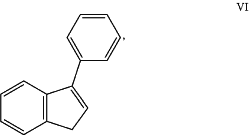 and
y represents the number of sp2 carbon atoms between M and the carbon atom bearing R3 and R4 and is 0 or 1,
with at least one co-catalyst of the general formula (1) in a molar ratio of the complex hydrogenation catalyst to the co-catalyst in the range of 1:(20-550)
CH2═CRR′ (1)
in which R is hydrogen and R′ represents
OR1 wherein R1 shall mean C1-C6-alkyl, C5-C6-cycloalkyl, C2-C6-alkenyl, C2-C6-alkynyl, phenyl, imidazolyl, triazolyl, or pyridinyl, —C(═O)(R2), —C(═O)N(R2)2, —[(CH2)nO]mR2, —[(CH2)nO]m—CH═CH2, or —(CH2)p—C(R3)2R4,
wherein
R2 are identical or different and represent H, C1-C6-alky, C5-C8-cycloalkyl, C2-C8-alkenyl, C2-C8-alkynyl, phenyl, imidazolyl, triazolyl, or pyridinyl,
R3 are identical or different and represent methyl, ethyl or —(CH2)n—O—CH═CH2,
R4 represents (CH2)p—O—CH═CH2,
n is 1, or 2,
m is 1, 2, or 3, and
p is 0, 1, or 3,
and thereafter
b) hydrogenating the nitrile rubber with hydrogen in the presence of the catalyst composition formed in step a).
|