| CPC C02F 1/4618 (2013.01) [C02F 1/46104 (2013.01); C25B 1/04 (2013.01); C25B 9/19 (2021.01); C25B 9/65 (2021.01); C25B 13/00 (2013.01); C25B 15/023 (2021.01); C02F 2201/4612 (2013.01); C02F 2201/4613 (2013.01); C02F 2201/4614 (2013.01); C02F 2201/46115 (2013.01); C02F 2201/46145 (2013.01)] | 6 Claims |
|
1. An electrolyzed water generating device comprising:
an electrolysis chamber for electrolyzing water so as to generate electrolyzed water,
a first feeding body and a second feeding body which are disposed in the electrolysis chamber and to which a DC voltage is applied, wherein a surface of the first feeding body and a surface of the second feeding body are formed of a hydrogen storage metal,
a diaphragm disposed between the first feeding body and the second feeding body to divide the electrolysis chamber into a first-polar chamber on the first feeding body side in which the first feeding body is disposed and a second-polar chamber on the second feeding body side in which the second feeding body is disposed,
a control unit for switching a polarity of the first feeding body and a polarity of the second feeding body into an anode and a cathode, respectively, or a cathode and an anode, respectively,
a flow rate sensor detecting an amount of flowing water into the electrolysis chamber on the cathode side per unit time,
a current detecting means detecting a DC current flowing between the first feeding body and the second feeding body,
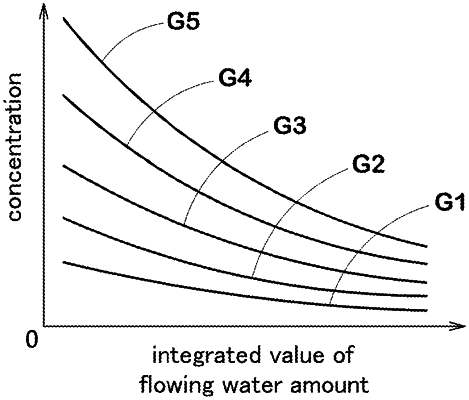
a memory in which reference data are stored, wherein, for each value of the DC current flowing between the first feeding body and the second feeding body,
a concentration of a hydrogen storage metal colloid contained in the electrolyzed water generated in the electrolysis chamber on the cathode side is obtained through experiments in advance as a function (G1, G2, G3, G4, G5) of an integrated value of the amount of flowing water into the electrolysis chamber on the cathode side, and
the obtained functions (G1, G2, G3, G4 and G5) are stored as the reference data, wherein each function is such that the concentration decreases as the integrated value increases,
a first water discharge channel for taking out the electrolyzed water generated in one of the first-polar chamber and the second-polar chamber which is on the cathode side,
a second water discharge channel for taking out the electrolyzed water generated in the other of the first-polar chamber and the second-polar chamber which is on the anode side, and
a flow channel switching valve for switching between
a connection state in which the first water discharge channel and the second water discharge channel are respectively connected to the first-polar chamber and the second-polar chamber, and
a connection state in which the first water discharge channel and the second water discharge channel are respectively connected to the second-polar chamber and the first-polar chamber,
wherein
when the electrolyzed water generating device is started and the flowing of water into the electrolyzed water generating device starts,
the control unit applies a DC voltage to the first feeding body and the second feeding body in a first polarity state or a second polarity state to start the electrolysis, wherein
the first polarity state is such that the first feeding body is positively charged and the first-polar chamber functions as an anode chamber, and the second feeding body is negatively charged and the second-polar chamber functions as a cathode chamber, and
the second polarity state is such that the first feeding body is negatively charged and the first-polar chamber functions as a cathode chamber, and the second feeding body is positively charged, and the second-polar chamber functions as an anode chamber,
at a predetermined timing, that is, when the flowing of water into the electrolyzed water generating device is started, or alternatively, when the flowing of water is stopped and the electrolysis is stopped,
the control unit switches the polarities of the first and second feeding bodies from the current polarity state to the invert polarity state,
the control unit calculates the concentration of the hydrogen storage metal colloid contained in the electrolyzed water generated in the electrolysis chamber on the cathode side based on a value of the DC current flowing between the first feeding body and the second feeding body and an integrated value of the amount of flowing water after switching the polarities of the first feeding body and the second feeding body by the control unit,
when calculating the concentration, the control unit refers to the reference data and the functions (G1, G2, G3, G4, G5) stored in the memory based on the DC current value, and the concentration is calculated by using the function (G1, G2, G3, G4, G5) corresponding to the DC current value and the integrated value of the amounts of flowing water.
|