| CPC A61B 5/05 (2013.01) [A61B 5/0507 (2013.01); H01Q 9/27 (2013.01); H01Q 1/36 (2013.01); H01Q 17/00 (2013.01); Y10T 29/49016 (2015.01)] | 18 Claims |
|
1. An electromagnetic (EM) probe for monitoring at least one biological tissue, comprising:
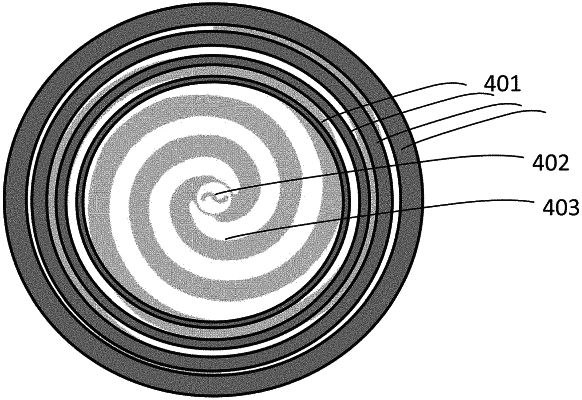
a spiral antenna having at least one spiral arm with a spiral path originated from a feeding point; and
an EM radiation absorbing layer mounted along a plurality of turnings of said at least one spiral arm of the antenna, said EM radiation absorbing layer having:
absorbing material between a plurality of gaps wherein the absorbing material is not present; and
wherein said EM radiation absorbing layer is formed such that a spiral propagation path of said at least one spiral arm passes via said plurality of gaps;
wherein the EM radiation absorbing layer is disposed in a plurality of concentric regions corresponding to portions of said spiral antenna having equal surface of antenna conductor;
wherein any of said plurality of concentric regions has an EM radiation absorption coefficient greater than any other of said plurality of concentric regions it encloses;
wherein an amount of the absorbing material disposed in each of said plurality of concentric regions gradually increases as a function of a distance of each of said plurality of concentric regions from said feeding point.
|