| CPC H04L 27/2663 (2013.01) [H04B 1/0003 (2013.01); H04L 27/266 (2013.01); H04W 56/001 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
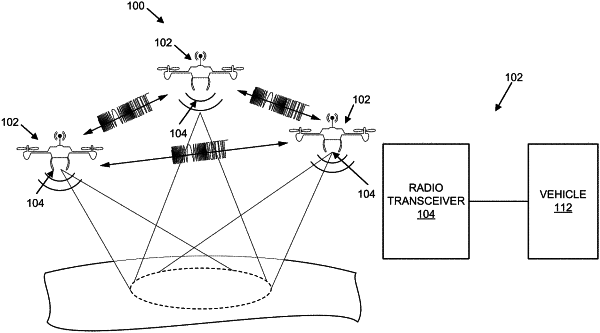
1. A method for providing wireless clock synchronization of multiple devices, the method comprising:
performing coarse synchronization by synchronizing clocks of each of the multiple devices using an independent clock source; and
performing fine clock synchronization by:
measuring pair-wise radio frequency (RF) time of flight using baseband waveform samples of each of the multiple devices based on the clocks of each of the multiple devices; and
applying at least one of (i) a fractional delay and (ii) a phase correction to the baseband waveform samples to cause the baseband waveform samples to replicate equivalently synchronized sample clocks.
|