| CPC H01M 4/139 (2013.01) [H01M 4/1391 (2013.01); H01M 4/624 (2013.01); H01M 10/052 (2013.01); H01M 10/4285 (2013.01); H01M 10/48 (2013.01); H01M 2004/028 (2013.01)] | 6 Claims |
|
1. A method for designing an electrode for a lithium secondary battery, the method comprising:
(1) manufacturing a plurality of electrodes each containing an active material, a binder, and a conductive agent, and having a different content of the conductive agent from each other;
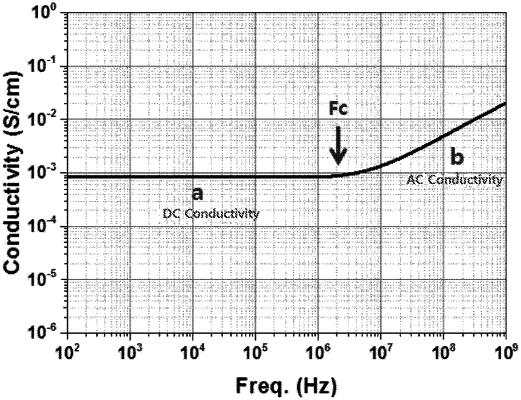
(2) applying an alternating current to each of the plurality of electrodes manufactured above while changing a frequency and using a broadband dielectric spectrometer (BDS) to measure conductivity of each of the electrodes;
(3) identifying a specific frequency (Fc) at a point at which the conductivity of each of the electrodes changes from a DC conductivity to an AC conductivity; and
(4) comparing the specific frequency (Fc) and a preset reference frequency (Fr) of 107 Hz to determine a deviation between the preset reference frequency (Fr) and the specific frequency (Fc), and determining a content of the conductive agent contained in an electrode is appropriate when the deviation is within a reference deviation of 3×106 Hz.
|