| CPC G06T 7/0012 (2013.01) [G06T 7/11 (2017.01); G06T 7/30 (2017.01); G06V 10/25 (2022.01); G06V 10/751 (2022.01); G06T 2207/20076 (2013.01); G06T 2207/20084 (2013.01); G06T 2207/30068 (2013.01); G06V 2201/03 (2022.01); G06V 2201/07 (2022.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A method, applied to an apparatus for mammographic multi-view mass identification, comprising:
receiving a main image, a first auxiliary image, and a second auxiliary image, wherein the main image and the first auxiliary image are images of a breast of a person, and the second auxiliary image is an image of another breast of the person;
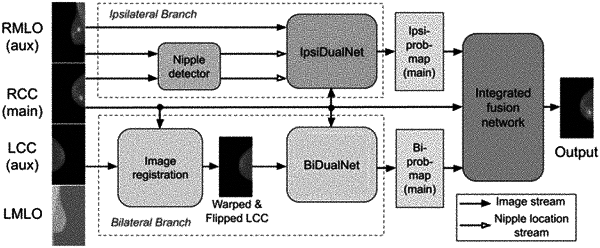
detecting a nipple location based on the main image and the first auxiliary image;
generating a first probability map of the main image based on the main image, the first auxiliary image, and the nipple location by an ipsilateral analyzer that is built on a Faster-RCNN detection architecture and configured for:
enabling two input branches to share same weights and extract features from the main image and the first auxiliary image in a same way, and
modelling relationships between two region of interests (RoIs) in a single image based on similarities in brightness, shapes, area sizes, and relative positions of the RoIs,
wherein a relative position of a RoI includes a distance from the RoI to the nipple location, and in a training process, focal loss and distance-intersection-over-union loss (DIoU) is used to improve performance of the ipsilateral analyzer;
generating a second probability map of the main image based on the main image, the second auxiliary image, and the nipple location; and
generating and outputting a fused probability map based on the first probability map and the second probability map.
|