| CPC G06T 5/002 (2013.01) [B60K 35/00 (2013.01); G06F 3/013 (2013.01); G06T 5/20 (2013.01); G06T 7/20 (2013.01); B60K 2370/149 (2019.05); B60K 2370/152 (2019.05); B60K 2370/21 (2019.05); B60K 2370/67 (2019.05); G06T 2207/30252 (2013.01); G06T 2207/30268 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
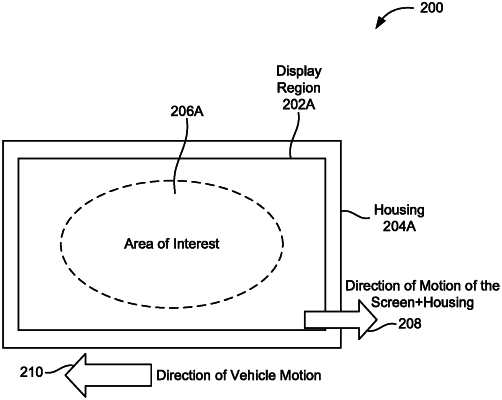
|
1. A computer-implemented method for generating a motion compensation signal, comprising:
collecting motion data associated with a vehicle progressing along a route using one or more environmental sensors, wherein the collected motion data is associated with data pertaining to a route ahead of the vehicle;
tracking eye movements of a user within a cabin of the vehicle along the route using the one or more environmental sensors, wherein the tracking is associated with the collected motion data;
processing the motion data and the eye movements to predict a motion event identified by the one or more environmental sensors and the tracking of the eye movements, the motion event related to an upcoming vehicle maneuver along the route of the vehicle, a direction of the eye movements of the user, and a timing of an occurrence of the eye movements in relation to the route ahead of the vehicle; and
generating the motion compensation signal based on the prediction of the motion event.
|