| CPC C07D 401/14 (2013.01) [A61K 9/0053 (2013.01); A61K 31/7072 (2013.01)] | 13 Claims |
|
1. A method comprising administering a compound of Formula (II) to a subject having a neurological disorder, wherein the compound of Formula (II) has the structure:
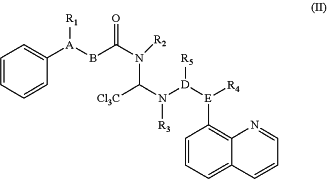 wherein R1 is H, R2 is H, R3 is H, R4 is H or null, R5 is —SR6, R6 is CH2(C3-6 cycloheteroalkyl), C3-6 cycloheteroalkyl, amino acid, amino acid derivative, C1-20 alkyl, or C1-20 heteroalkyl, A-B is C═CH, and D-E is CH—N or C═N; and
wherein the neurological disorder is amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), multiple sclerosis (MS), Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, Huntington's disease, prion-associated disease, spinocerebellar ataxia, or spinal muscular atrophy.
|