| CPC H04L 27/0012 (2013.01) [H04W 84/18 (2013.01)] | 17 Claims |
|
1. A system, comprising:
a transmitting node configured to:
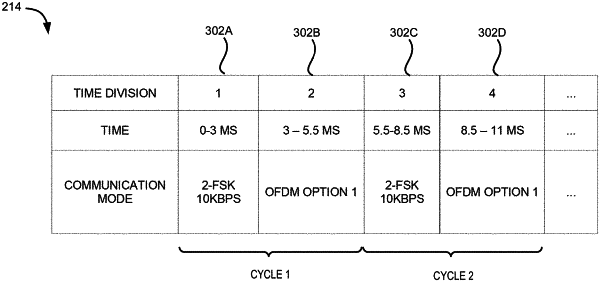
determine a scheduled communication mode of an upcoming time division according to a time-division schedule, wherein the time-division schedule comprises a plurality of cycles, each cycle comprising at least two time divisions and specifying respective scheduled communication modes for the at least two time divisions;
determine that the scheduled communication mode of the upcoming time division matches a selected communication mode from a plurality of supported communication modes by both the transmitting node and a receiving node, the selected communication mode being determined based on communication conditions of the transmitting node and the receiving node;
in response to determining that the upcoming time division has arrived and becomes a current time division, generate and transmit a data packet to the receiving node using the scheduled communication mode;
determine that the selected communication mode is different from any scheduled communication mode in the time-division schedule;
generate and transmit a mode switch header in the scheduled communication mode of the current time division to indicate the selected communication mode; and
transmit the data packet in the selected communication mode; and
the receiving node configured to:
operate in the scheduled communication mode specified for the current time division by the time-division schedule;
while operating in the scheduled communication mode, determine that a preamble of the data packet is detected in the current time division; and
based, at least in part, upon determining that the preamble of the data packet is detected, receive and process a remaining portion of the data packet in the scheduled communication mode.
|