| CPC G11C 11/5628 (2013.01) [G06N 3/063 (2013.01); G06N 3/084 (2013.01)] | 19 Claims |
|
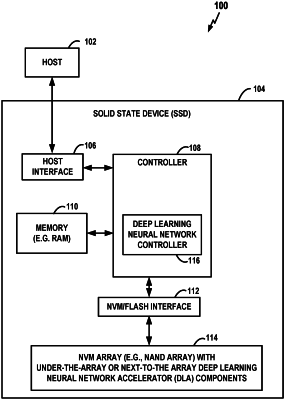
1. An apparatus comprising:
non-volatile memory (NVM) NAND elements formed in a memory array including one or more memory dies, the NVM NAND elements including single-bit-per-cell elements and multiple-bit-per-cell elements;
a neural network computing component formed on or in at least one memory die of the memory array and coupled to the NVM NAND elements, the neural network computing component configured to perform neural network computing operations;
a read-modify-write component formed on or in the at least one memory die and configured to obtain neural network training data from a memory external to the memory array, read synaptic weights from the NVM NAND elements of the memory array, update the synaptic weights using the neural network computing component based on the training data, and store the updated synaptic weights in the single-bit-per cell elements of the memory array; and
an on-chip copy with update component formed on or in the at least one memory die and configured to perform an on-chip copy of the updated synaptic weights stored in the NVM NAND elements, wherein the on-chip copy with update component is further configured to perform a fold operation in which the updated synaptic weights are read from a plurality of the single-bit-per-cell elements of the memory array, are further updated in a neural network computing operation using the neural network computing component, and are folded into at least one of the multiple-bit-per-cell elements of the memory array.
|