| CPC G09G 3/3607 (2013.01) [G09G 3/3696 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A voltage adjustment method for a display panel, comprising:
detecting whether an absolute value of a difference between a first gray scale data of a first sub pixel and a second gray scale data of a second sub pixel is larger than a preset gray scale threshold, wherein the first gray scale data of the first sub pixel and the second gray scale data of the second sub pixel are in a static picture area of a same image to be displayed, and the first sub pixel and the second sub pixel are driven by a same data line and are arranged adjacent to each other;
acquiring the first gray scale data when the absolute value of the difference between the first gray scale data of the first sub pixel and the second gray scale data of the second sub pixel is larger than the preset gray scale threshold; and
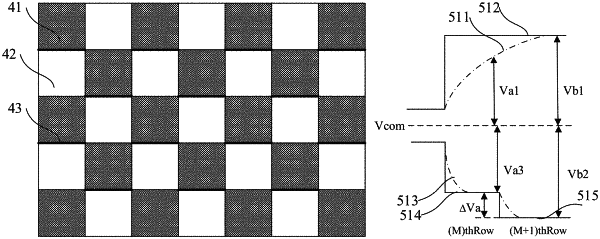
inputting a target data voltage to the data line coupled to the first sub pixel according to the first gray scale data, so as to adjust an original pixel voltage to be theoretically charged to the first sub pixel into a target pixel voltage and to cause an absolute value of a voltage difference between a first voltage difference of the first sub pixel in a positive frame and a second voltage difference of the first sub pixel in a negative frame, to be smaller than a preset voltage difference threshold;
wherein the first voltage difference is an absolute value of a voltage difference between the target pixel voltage of the first sub pixel in the positive frame and a common voltage, and the second voltage difference is an absolute value of a voltage difference between the target pixel voltage of the first sub pixel in the negative frame and the common voltage,
wherein the positive frame and the negative frame are two adjacent frames during which polarities of voltages applied to liquid crystal molecules are opposite to each other; and
the original data voltage of the first sub pixel in only the positive frame is adjusted to the target data voltage in the positive frame, so that the original pixel voltage in the positive frame is adjusted to the target pixel voltage in the positive frame, while the target pixel voltage in the negative frame is equal to the original pixel voltage in the negative frame, wherein the first voltage difference is greater than an absolute value of a voltage difference between the original pixel voltage in the positive frame and the common voltage; or the original data voltage of the first sub pixel in only the negative frame is adjusted to the target data voltage in the negative frame, so that the original pixel voltage in the negative frame is adjusted to the target pixel voltage in the negative frame, while the target pixel voltage in the positive frame is equal to the original pixel voltage in the positive frame, the second voltage difference is less than an absolute value of a voltage difference between the original pixel voltage in the positive frame and the common voltage,
wherein the absolute value of the voltage difference between the target pixel voltage of the first sub pixel in the positive frame and the common voltage during the positive frame driving is equal to the absolute value of the voltage difference between the target pixel voltage of the first sub pixel in the negative frame and the common voltage during the negative frame driving.
|