| CPC G06T 7/10 (2017.01) [G06T 2207/10016 (2013.01); G06T 2207/10132 (2013.01); G06T 2207/20081 (2013.01); G06T 2207/30048 (2013.01); G06T 2207/30104 (2013.01)] | 10 Claims |
|
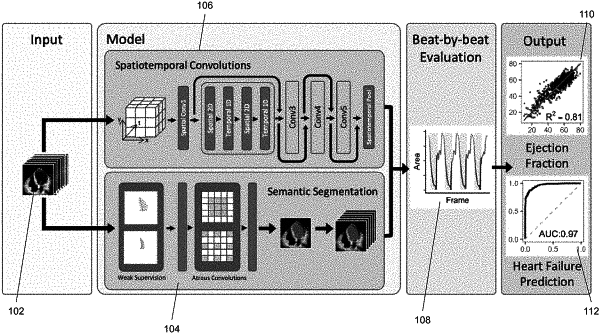
1. A method for analyzing images obtained from an echocardiogram, comprising:
obtaining a cardiac ultrasound video of an individual's heart illustrating at least one view of a heart of the patient and comprising a plurality of cardiac cycles;
assessing at least one cardiac parameter based on the cardiac ultrasound video, comprising:
using a first machine learning model comprising spatiotemporal convolutions,
using a second machine learning model comprising atrous convolutions, to generate frame-level semantic segmentation of a left ventricle throughout a cardiac cycle, and
performing a beat-by-beat evaluation based on the spatiotemporal convolution and semantic segmentation to generate a plurality of clips of frames, wherein each clip of frames in the plurality of clips of frames represents one cardiac cycle and determining an ejection fraction for each cardiac cycle; and
outputting an average ejection fraction of the heart for the patient based on the plurality of clips of frames.
|