| CPC G06N 5/01 (2023.01) [G06F 16/29 (2019.01); G06F 18/214 (2023.01); G06F 18/217 (2023.01); G06F 18/2414 (2023.01); G06F 18/24323 (2023.01); G06N 20/00 (2019.01); G06Q 50/02 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A method for identifying ground types from one or more interpolated covariates, the method comprising:
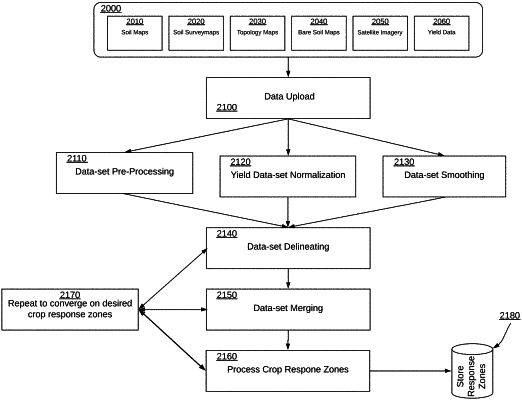
providing a geospatial database associated with a crop prediction engine, wherein the geospatial database receives a plurality of soil composition information for each of a plurality of plots of land;
accessing the plurality of soil composition information for each of the plurality of plots of land, in which the soil composition information includes at least one of a plurality of measured soil sample results, a plurality of environmental results, and a plurality of soil conductivity results;
identifying a plurality of covariates from the plurality of soil composition information;
interpolating, at the crop prediction engine, covariates associated with a plurality of different locations with an interpolation training model;
generating a plurality of voxels, wherein each voxel associates the one or more interpolated covariates with a corresponding geographical location within at least one of the plurality of plots of land;
training a random forest training model with the interpolated covariates;
traversing the voxels through the trained random forest model to identify one or more clusters of voxels that are co-associated; and
identifying a ground type by combining the one or more co-associated clusters, wherein each ground type is associated with at least one of a crop zone, a soil fertility, and a farm management recommendation.
|