| CPC G01J 3/2889 (2013.01) [G01J 3/10 (2013.01); G01J 3/4406 (2013.01)] | 15 Claims |
|
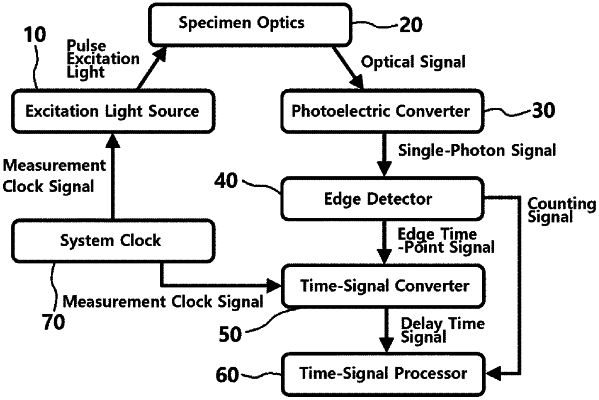
1. A time-resolved single-photon counting apparatus, comprising:
an excitation light source for generating pulsed excitation light;
a specimen optics for collecting an optical signal produced by irradiating the pulsed excitation light to a specimen;
a photoelectric converter for photoelectrically converting the optical signal to generate an analog single-photon signal;
an analog-to-digital (AD) signal converter for sampling the analog single-photon signal to convert the same into a digital single-photon signal;
a digital photon-discrimination and timing detector for generating a photon-discrimination signal by discriminating the single-photon property of the digital single-photon signal and generating a delay time signal having delay time information by measuring a pulse time point of the digital single-photon signal; and
a time-signal processor for counting valid single-photon detection events according to the delay time with reference to the photon-discrimination signal,
wherein the digital photon-discrimination and timing detector generates a photon-discrimination signal obtained by discriminating the single-photon property for the digital single-photon signal based on the characteristics of a temporal voltage waveform provided by the digital single-photon signal,
wherein the delay time information is relative time information of a pulse time point of the digital single-photon signal with respect to a pulse generation time point of the pulsed excitation light, and
wherein the time-signal processor discriminates as the valid single-photon detection event when the photon-discrimination information is in the state of a true single-photon property or single-photon detection.
|