| CPC C30B 15/04 (2013.01) [C30B 15/10 (2013.01); C30B 29/06 (2013.01); C30B 35/002 (2013.01); C30B 35/007 (2013.01); H01L 21/02002 (2013.01)] | 3 Claims |
|
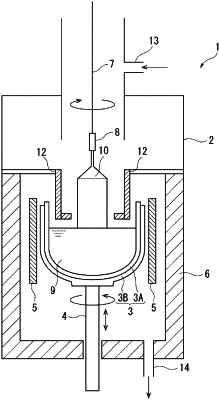
1. A producing method of an n-type monocrystalline silicon by pulling up the n-type monocrystalline silicon from a silicon melt comprising a main dopant in a form of red phosphorus and growing the n-type monocrystalline silicon according to a Czochralski process,
wherein:
the n-type monocrystalline silicon comprises a straight-body diameter ranging from 301 mm to 330 mm, and
the n-type monocrystalline silicon, a part of which exhibits an electrical resistivity ranging from 0.8 mΩcm to 1.0 mΩcm, is pulled up using a quartz crucible whose inner diameter ranges from 1.7-fold to 2.0-fold relative to a straight-body diameter of the n-type monocrystalline silicon.
|