| CPC C23C 16/26 (2013.01) [C23C 16/00 (2013.01); C23C 16/0272 (2013.01); C23C 16/22 (2013.01); C23C 28/00 (2013.01); C23C 28/046 (2013.01); Y10T 428/31663 (2015.04)] | 34 Claims |
|
1. A carbonaceous coating for a passive electrical component for protecting the passive electrical component from an attack by ammonia comprising:
(i) a sol-gel layer which is producible or has been produced by a sol-gel method or
(ii) a plasma-polymeric layer which is producible or has been produced by plasma-activated chemical vapor deposition;
wherein each of (i) the sol-gel layer or (ii) the plasma polymeric layer has a surface facing away from the passive electrical component, and
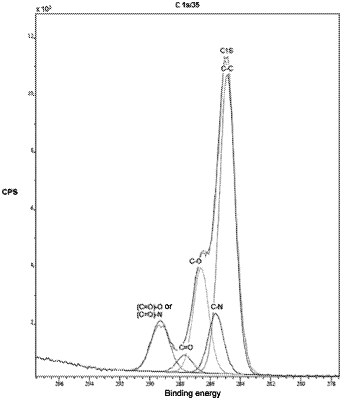
comprises a carbon content of 50 to 90 atom % at a depth of 80 nm below the surface and as measured by and based on a total number of atoms detected by XPS, or
comprises an organometallic layer comprising a carbon content of 2 to 50 atom % at a depth of 80 nm below the surface and as measured by and based on the total number of atoms detected by XPS; wherein
each of (i) the sol-gel layer or (ii) the plasma polymeric layer has at least one hydrolyzable group on the surface, the at least one hydrolyzable group being selected from the group consisting of ester, amide, urethane and urea groups, and
(i) the sol-gel layer comprises a hydrolyzable carbon content of ≤15 atom % or (ii) the plasma-polymeric layer comprises a hydrolyzable carbon content of ≤10 atom %, wherein hydrolyzable carbon content is the portion of carbon within the at least one hydrolyzable group on the surface relative to the total carbon content on the surface as measured by XPS with C1s peak fitting.
|