| CPC B05D 1/204 (2013.01) [B05D 7/24 (2013.01); C09D 5/22 (2013.01); C09K 11/08 (2013.01)] | 11 Claims |
|
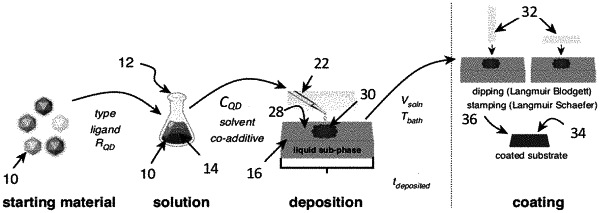
1. A method of forming a nanoparticle monolayer by controlling a nanoparticle solution spreading rate and a solvent evaporation rate, the method comprising the steps of:
selecting a solvent for a nanoparticle solution, the nanoparticle solution comprising the solvent and nanoparticles, wherein the solvent has a solvent vapor pressure and a solvent surface tension;
selecting a sub-phase base and an additive for a sub-phase solution, the sub-phase solution contained within a vessel and comprising the sub-phase base and the additive, wherein the sub-phase solution has a viscosity, a surface tension, and a density and wherein the vessel is within a controlled environment to control a total pressure, partial pressures of gas species, and temperatures of the sub-phase solution and/or the nanoparticle solution; and
depositing a volume of the nanoparticle solution onto a top surface of the sub-phase solution, the volume of the nanoparticle solution being unconstrained by walls of the vessel, such that the nanoparticle solution spreads at the nanoparticle solution spreading rate and the solvent evaporates at the solvent evaporation rate to form a uniform nanoparticle monolayer on the top surface of the sub-phase solution, wherein the nanoparticle solution spreading rate is controlled by the sub-phase solution viscosity, the sub-phase solution density, and the interfacial surface tensions of the solvent and sub-phase solution, and wherein the solvent evaporation rate is controlled by the solvent vapor pressure, the sub-phase solution temperature, and the controlled environment.
|