| CPC A61M 25/09 (2013.01) [A61M 25/0905 (2013.01); A61M 25/09033 (2013.01); A61M 2025/09083 (2013.01); A61M 2025/09133 (2013.01); A61M 2025/09158 (2013.01); A61M 2205/0266 (2013.01); A61M 2205/0272 (2013.01); A61M 2205/0283 (2013.01); A61M 2205/0294 (2013.01); A61M 2205/8262 (2013.01)] | 11 Claims |
|
1. A guidewire device comprising:
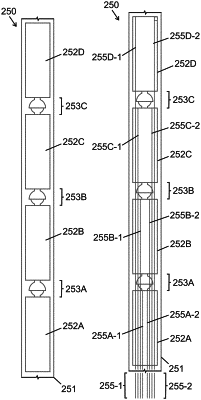
a tube having a longitudinal axis, a first end, a second end, and an interior;
a plurality of body elements and a plurality of pivot joints sequentially arranged in a longitudinal direction within the interior of the tube between the first end and the second end, wherein each body element of the plurality of body elements is connected to at least one other body element via at least one pivot joint of the plurality of pivot joints;
a plurality of tensile elements extending in the longitudinal direction through the tube from the first end toward the plurality of body elements, wherein different tensile elements of the plurality of tensile elements terminate at different body elements of the plurality of body elements, are separately operable to cause pivotal movement between different body elements of the plurality of body elements, thereby permitting adjustment of an angle or curvature of the guidewire device at multiple positions along the longitudinal axis; and
a plurality of radially contractible fiber regions arranged in or on the tube, wherein each radially contractible fiber region of the plurality of radially contractible fiber regions is longitudinally spaced from each other radially contractible fiber region.
|