| CPC A61B 8/4416 (2013.01) [A61B 5/0035 (2013.01); A61B 5/0066 (2013.01); A61B 5/0084 (2013.01); A61B 5/6852 (2013.01); A61B 8/12 (2013.01); A61B 2562/0204 (2013.01); A61B 2562/0233 (2013.01)] | 24 Claims |
|
1. An image data collection system comprising:
a data collection probe to be inserted in a patient comprising:
a sheath;
a torque wire;
a radiopaque marker comprising a first end and a second end, the first end attached to the torque wire;
a probe tip comprising:
a backing material support comprising:
an ultrasound absorbing material;
an elongate section defining a channel;
an angled support section adjacent the elongate section, wherein a distal end of the channel is defined by the ultrasound absorbing material forming the angled support section;
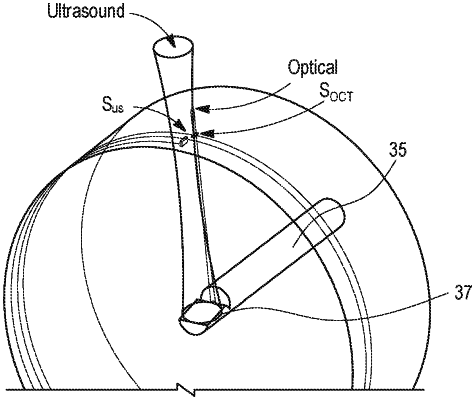
an optical data collection subsystem comprising an optical fiber and a beam director configured to direct a light beam having an optical center axis, the beam director angled to direct the light beam at an angle ranging from 5 degrees to 20 degrees relative to a normal of a longitudinal axis of the optical fiber; and
an acoustic data collection subsystem comprising an ultrasonic transducer having a distal end and a proximal end, the ultrasonic transducer supported by the angled support section and angled to direct an acoustic wave having an acoustic center axis at an angle ranging from 5 degrees to 15 degrees relative to the normal of the longitudinal axis of the optical fiber, wherein the probe tip, the radiopaque marker, and the torque wire are disposed in the sheath, and wherein the beam director and the ultrasonic transducer are axially displaced such that the beam director is disposed completely between the second end of the radiopaque marker and the proximal end of the ultrasonic transducer and such that the optical center axis and the acoustic center axis are spaced from one another in the axial direction a distance between about 300 to about 500 microns;
a patient interface unit including a motor arranged to retract the probe tip at a pullback rate that ranges from about 18 mm/second to about 50 mm/second and to rotate the data collection probe at a rate of rotation that ranges from about 100 Hz to about 200 Hz; and
a controller that adjusts the pullback rate and the rate of rotation such that a time period between when the optical center axis and the acoustic center axis cross a common reference point is based on a cardiac cycle of the patient.
|