| CPC H04W 16/14 (2013.01) [H04L 1/0003 (2013.01); H04L 5/0005 (2013.01); H04W 72/0453 (2013.01); H04W 72/1263 (2013.01); H04W 72/27 (2023.01)] | 11 Claims |
|
1. A cross-scheduling resource allocation method for non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA)-based dynamic spectrum sharing (DSS) of a first wireless carrier according to a first wireless technology protocol with a second wireless carrier according to a second wireless technology protocol, the second wireless technology protocol being different from the first wireless technology protocol, and the first and second wireless carriers co-existing on a same target communication channel of an access network, the method comprising the steps of:
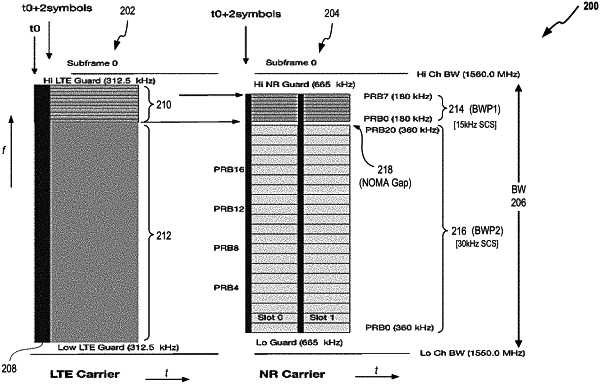
providing a resource subframe, within the target communication channel, to the first wireless carrier, wherein the resource subframe includes a specified frequency bandwidth and a specified time duration;
synchronizing the second wireless carrier (i) to the specified time duration of the resource subframe, and (ii) within the specified frequency bandwidth;
allocating (i) one or more first physical resource blocks (PRBs), within a first portion of the specified frequency bandwidth, for first user traffic transmitted according to the first technology protocol, and (ii) one or more second PRBs, within a second portion of the specified frequency bandwidth, for second user traffic transmitted according to the second technology protocol, wherein the first and second portions of the specified frequency bandwidth do not overlap;
programming a frequency gap between the first PRBs and the second PRBs;
obtaining channel information regarding the target communication channel; and
dynamically adjusting the programmed frequency gap based on the obtained channel information.
|