| CPC H04L 27/0014 (2013.01) [H04L 7/0054 (2013.01); H04L 27/106 (2013.01)] | 3 Claims |
|
1. A time-frequency joint synchronization method based on an all-phase spectrum-corrected Costas sequence, comprising:
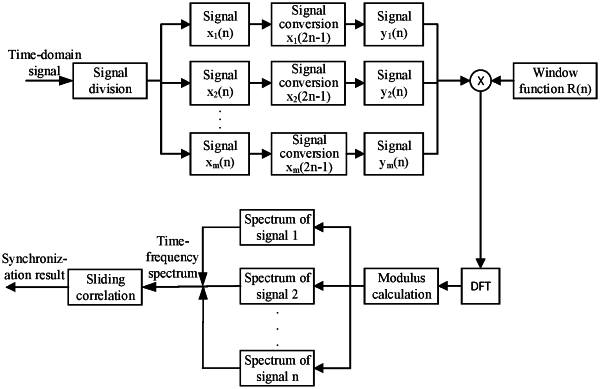
S1, dividing, by a receiver after receiving a time-domain signal x(N), the time-domain signal x(N) to obtain divided signals x1(n), x2(n), . . . , and xm(n) based on a time period of a symbol, wherein the divided signals are represented by xi(n), i=1, 2, . . . , m, and m represents the number of the divided signals;
S2, inverting the xi(n), windowing the inverted xi(n), performing an all-phase Fourier transform apFFT on the windowed xi(n) to obtain all-phase Fourier transforms X1(W) to Xm(W) of the divided signals xi(n), and performing modulus calculation to obtain spectrums |X1(W)|2 to |Xm(W)|2 of the divided signals xi(n), wherein the spectrums are represented by |Xi(W)|2;
S3, combining the spectrums |X1(W)|2 to |Xm(W)|2 of the divided signals into a time-frequency spectrum, and expressing the combined time-frequency spectrum as a time-frequency matrix;
S4, performing sliding autocorrelation on a local Costas sequence based on the time-frequency matrix by using a sliding window algorithm to obtain a two-dimensional autocorrelation function, obtaining a coarse synchronization result based on coordinates of a peak of the autocorrelation function, and correcting a discrete spectrum after all-phase Fourier transform based on a coarse estimation value to obtain a time delay estimation value and a frequency offset estimation value;
S5, determining whether an amplitude of the peak of the two-dimensional autocorrelation function in the S4 is decreased compared with an amplitude of a peak of a two-dimensional autocorrelation function in S4 in a previous iteration or whether the number of iterations reaches a maximum limit, outputting a time delay estimation value and a frequency offset estimation value in the S4 in the previous iteration as an output result of the method in a case that the amplitude of the peak of the two-dimensional autocorrelation function is decreased or the number of the iterations reaches the maximum limit, and increasing the number of iterations by one and proceeding to S6 in a case that the amplitude of the peak of the two-dimensional autocorrelation function is not decreased; and
S6, performing time delay correction and frequency offset correction on the time-domain signal x(N) in S1 by using the time delay estimation value and the frequency offset estimation value obtained in S4 as correction values to obtain a corrected time-domain signal x(N), and proceeding to S1.
|