| CPC G10H 1/0091 (2013.01) [G10K 15/08 (2013.01); G10H 2250/105 (2013.01); G10H 2250/115 (2013.01)] | 14 Claims |
|
1. An effect addition device comprising:
at least one processor,
wherein the at least one processor executes:
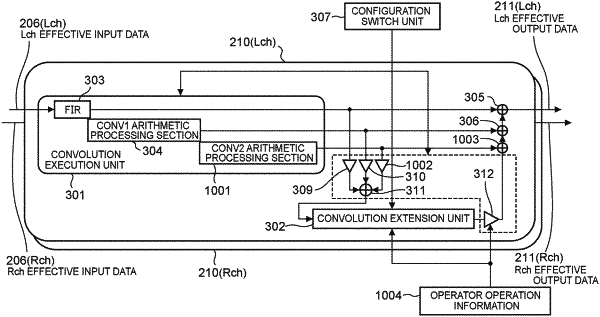
a time domain convolution process of convolving a first time domain data part of impulse response data of sound effects with time domain data on an original sound by time domain FIR (Finite Impulse Response) arithmetic processing which is executed in units of sampling periods;
a frequency domain convolution process of convoluting a second time domain data part of the impulse response data with the time domain data on the original sound by frequency domain arithmetic processing using a fast Fourier transform arithmetic operation in units of blocks of a predetermined time length respectively;
a convolution extension process of extending a convolved state or states of an output signal or output signals which is/are output as a result of execution of either the time domain convolution process or the frequency domain convolution process or both of the time domain convolution process and the frequency domain convolution process at least by either one type of arithmetic processing which corresponds to an all-pass filter or arithmetic processing which corresponds to a comb filter or both types of the arithmetic processing in a time range which exceeds a time width of the impulse response data; and
a synthesized sound effect addition process of adding a sound effect which is synthesized by execution of the time domain convolution process, the frequency domain convolution process, and the convolution extension process to the original sound, and
wherein the at least one processor:
convolves a front-half time domain data part in the time width of the impulse response data with the time domain data on the original sound by the time domain FIR arithmetic processing which is executed in units of the sampling periods in the time domain convolution process,
convolves a rear-half time domain data part in the time width of the impulse response data with the time domain data on the original sound by the frequency domain arithmetic processing using the fast Fourier transform arithmetic operation in units of blocks of the predetermined time length respectively in the frequency domain convolution process, and
extends the convolved states of the output signals which are output as the result of execution of both of the time domain convolution process and the frequency domain convolution process at least by either the arithmetic processing which corresponds to the all-pass filter or the arithmetic processing which corresponds to the comb filter or both types of the arithmetic processing in the time range which exceeds the time width of the impulse response data in the convolution extension process.
|