| CPC G01N 33/743 (2013.01) [C07K 14/00 (2013.01); C12N 9/22 (2013.01); C12N 15/11 (2013.01); C12N 15/62 (2013.01); C12N 15/63 (2013.01); C12N 15/902 (2013.01); C07K 2319/00 (2013.01); C12N 2310/20 (2017.05); C12N 2320/50 (2013.01); C12N 2800/22 (2013.01); C12N 2800/80 (2013.01)] | 9 Claims |
|
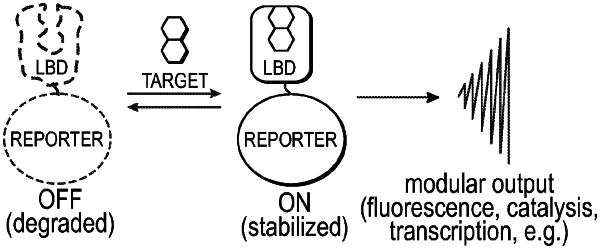
1. A conditionally stable biosensor comprising a homodimeric ligand binding domain (LBD) having conditionally-destabilizing mutations that is fused to a trans-activation domain (TAD) and a DNA binding domain (DBD), wherein the conditionally stable biosensor is stabilized when the ligand binding domain is bound to a cognate steroid, and wherein the DNA binding domain (DBD) binds to DNA and the trans-activation domain (TAD) activates transcription of a target gene.
|