| CPC E05B 77/54 (2013.01) [B60R 16/023 (2013.01); G05B 9/02 (2013.01); E05Y 2400/45 (2013.01); E05Y 2400/52 (2013.01); E05Y 2900/512 (2013.01)] | 22 Claims |
|
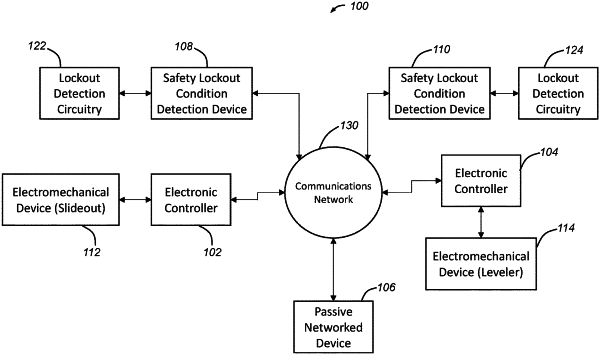
1. A method for controlling an electromechanical operation of an electromechanical device based on a safety lockout condition determined using a distributed safety lockout system, the distributed safety lockout system comprising a plurality of networked devices communicatively coupled via a communications network, the plurality of networked devices including one or more electronic controllers and a plurality of safety lockout condition detection devices; the method comprising:
at one or more of the plurality of networked devices:
receiving a safety lockout status from another networked device via the communications bus;
comparing a local safety lockout status to the received safety lockout status;
determining whether to update the local safety lockout status based on results of comparing the local safety lockout status to the received safety lockout status and, when it is determined to update the local safety lockout status, then updating the local safety lockout status to the received safety lockout status; and
broadcasting the local safety lockout status over the communications bus;
at one or more of the plurality of safety lockout condition detection devices:
determining a proposed safety lockout status based on sensor data obtained by the safety lockout device;
comparing the proposed safety lockout status to the local safety lockout status and/or a received safety lockout status that is received from another networked device over the communications bus; and
determining an updated local safety lockout status to be the local safety lockout status based on comparing the proposed safety lockout status to the local safety lockout status and/or the received safety lockout status; and
at any of the one or more electronic controllers, controlling an electromechanical operation of an electromechanical device based on the local safety lockout status.
|