| CPC C12Q 1/6874 (2013.01) [C12N 15/1065 (2013.01); C12Q 1/689 (2013.01); C12Q 1/6869 (2013.01); G16B 30/00 (2019.02); G16B 30/10 (2019.02); C12Q 2600/166 (2013.01)] | 49 Claims |
|
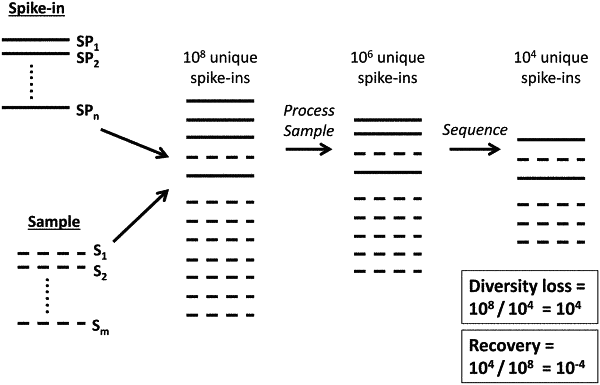
1. A method of determining abundance of nucleic acids in an initial sample comprising target nucleic acids, the method comprising:
(a) adding a known quantity of spike-in nucleic acids to the initial sample comprising target nucleic acids, wherein the spike-in nucleic acids comprise at least 1,000 spike-in nucleic acids with sequences that are unique to each other;
(b) performing a sequencing assay on a portion of the target nucleic acids and a portion of the at least 1000 spike-in nucleic acids, thereby obtaining target nucleic acid sequence reads and spike-in nucleic acid sequence reads; and
(c) using the spike-in nucleic acid sequence reads to calculate abundance of the target nucleic acids.
|