| CPC A61F 2/004 (2013.01) [A61F 2/04 (2013.01); A61B 2017/00805 (2013.01); A61F 2/0045 (2013.01); A61F 2002/047 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. An implantable device kit for controllable coaptation of a body lumen in tissue of a living body, comprising:
two implantable devices each including:
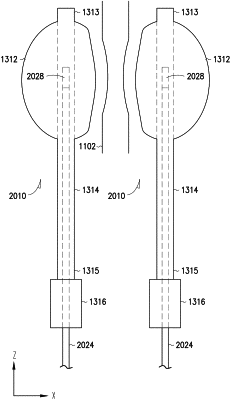
an adjustable membrane element including a continuous wall having an inner surface defining a chamber, the adjustable membrane element configured to coapt the body lumen;
an elongate conduit including a conduit peripheral surface, a conduit rear end, a conduit front end, and a conduit lumen, the conduit peripheral surface connected to and sealed to the adjustable membrane element at or near the conduit front end, the conduit lumen having a first opening at the conduit rear end, a second opening in fluid communication with the chamber; and a closed end at or near the conduit front end; and
a rear port connected to the conduit rear end and including a cavity in fluid communication with the first opening of the conduit lumen; and
two sensor probes each configured to be partially placed in one implantable device of the two implantable devices and each including:
a probe front end having a sharp tip and configured to enter the conduit lumen of the one implantable device by piercing through the rear port of the one implantable device and reach the closed end of the conduit lumen; and
a sensor configured to detect information indicative of a degree of the coaptation of the body lumen,
wherein the two implantable devices are each configured to be completely enclosed within the tissue by implantation with the adjustable membrane element adjacent the body lumen.
|