| CPC A61B 5/4812 (2013.01) [A61B 5/0205 (2013.01); A61B 5/05 (2013.01); A61B 5/4818 (2013.01)] | 14 Claims |
|
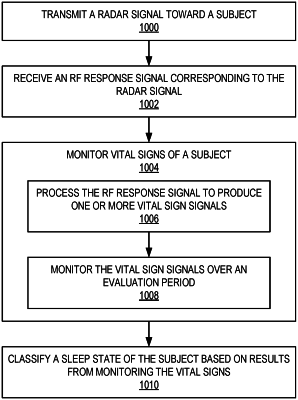
1. A method for remote sleep monitoring, the method comprising:
transmitting a radar signal toward a subject;
receiving a radio frequency (RF) response signal corresponding to the radar signal;
monitoring vital signs of a subject, the vital signs comprising a respiratory signal and a cardiac signal, the monitoring of the vital signs comprising:
processing the RF response signal, the processing comprising:
producing vital sign signals, the vital sign signals comprising the respiratory signal and a mixed respiratory and cardiac spatial channel;
extracting the cardiac signal from the mixed respiratory and cardiac spatial channel;
producing spatio-temporal data of motion response in the RF response signal; and
range gating the spatio-temporal data to produce a plurality of spatial channels comprising one or more respiratory spatial channels and one or more mixed respiratory and cardiac spatial channels; and
monitoring the vital sign signals over an evaluation period; and
classifying a sleep state of the subject based on results from monitoring the vital signs.
|